The Earth, a celestial marvel, is a complex entity with various components shaping its form. Among these concepts, the geoid stands as a fundamental notion that significantly influences our understanding of the planet’s shape and structure. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the concept of the geoid, exploring its importance and the profound insights it offers regarding the Earth’s shape.
The Earth’s Shape: Beyond a Simple Sphere
The prevailing notion that the Earth is a perfectly round sphere often falls short when scrutinized under scientific lenses. This is where the concept of the geoid comes into play.
Understanding the Geoid’s Definition
The geoid can be defined as the hypothetical surface that coincides with the mean sea level of the Earth’s oceans. In simpler terms, it represents the shape that the Earth’s oceans would take under the influence of gravity and rotation, disregarding the perturbations caused by factors like tides and currents.
Deviations from the Ideal Shape
Contrary to the simplistic view of a spherical Earth, the geoid reveals deviations and undulations on the planet’s surface. These deviations arise due to the uneven distribution of mass, such as variations in density and topographical features. The geoid acts as a reference surface, allowing scientists to comprehend these irregularities and study the gravitational field.
Significance of the Geoid
The geoid isn’t just a theoretical concept; it has immense practical significance in various fields.
Geodetic Surveys and Mapping
Surveyors and cartographers heavily rely on the geoid to create accurate maps and navigation systems. By accounting for the Earth’s deviations from a perfect sphere, they can ensure precise measurements of distances and elevations.
Gravity and Earth’s Interior
Studying the geoid aids in unraveling the Earth’s internal structure and the distribution of mass beneath its surface. Variations in the gravitational field, as depicted by the geoid, provide insights into the movement of tectonic plates and the composition of the Earth’s interior.
Global Sea Level Monitoring
The geoid plays a crucial role in monitoring changes in global sea levels. By comparing satellite measurements to the geoid’s shape, scientists can identify regions experiencing rising sea levels due to factors like melting ice caps and thermal expansion.

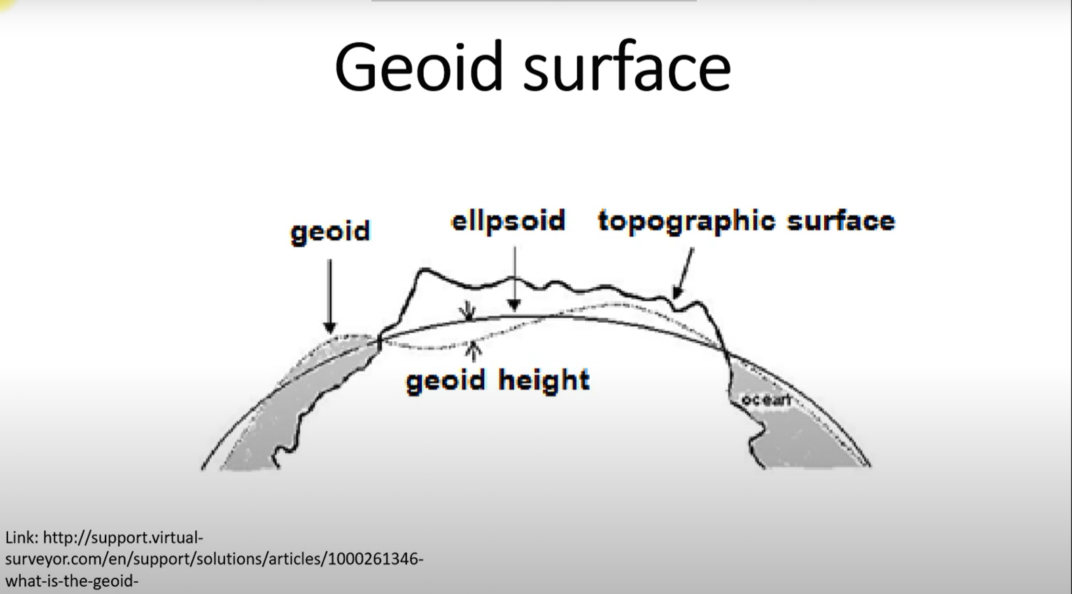
Geoid vs. Ellipsoid: Unveiling the Differences
To better grasp the concept of the geoid, it’s essential to differentiate it from another pivotal reference: the ellipsoid.
Ellipsoidal Earth Model
The ellipsoidal model approximates the Earth’s shape as an ellipsoid—a three-dimensional shape resembling a slightly flattened sphere. This model serves as a simplified representation and is commonly used in navigation systems.
Contrasting the Geoid and the Ellipsoid
The key distinction lies in the fact that the ellipsoid assumes a uniform distribution of mass, ignoring the actual irregularities on the Earth’s surface. On the other hand, the geoid takes into account these irregularities, showcasing the true gravitational equipotential surface.
Geoid Determination and Measurement
Measuring the geoid involves advanced technologies and meticulous calculations.
Satellite Gravimetry
Satellite missions equipped with gravimetric instruments play a pivotal role in measuring the geoid’s shape. These instruments detect minute variations in gravitational acceleration across the Earth’s surface, allowing scientists to create accurate geoid models.
Global Geopotential Models
Geophysicists employ complex mathematical models to compute the Earth’s geopotential—a representation of the Earth’s gravitational potential energy. These models aid in generating geoid surfaces that reflect the planet’s gravitational anomalies.
Exploring Geoid’s Real-World Applications
The implications of the geoid stretch far beyond theoretical concepts.
Aiding Navigation Systems
Navigation systems, both on land and in the air, leverage the geoid’s data to provide accurate positioning information. This ensures that vehicles and aircraft can traverse the planet with precision, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Understanding Ocean Circulation
The geoid assists in understanding ocean circulation patterns. By comprehending the gravitational forces influencing ocean currents, scientists can predict the movement of marine masses, influencing climate studies and marine navigation.
Determining Geoid’s Role in Earth Sciences
The geoid’s intricate relationship with gravitational variations serves as a valuable tool for earth scientists. It aids in researching phenomena such as isostasy—the balance between the Earth’s crust and underlying mantle.
Geoid and Beyond: A Glimpse into Future Research
The study of the geoid continues to evolve, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries.
Geodesy Advancements
Advancements in geodetic techniques and technologies promise more accurate geoid models, enhancing our understanding of the Earth’s shape and gravitational field.
Space Exploration
The geoid’s insights aren’t confined to Earth alone. Researchers utilize geoid data to study the shapes of other celestial bodies, enhancing our comprehension of the broader cosmos.
Climate Change Analysis
As the planet undergoes environmental shifts, the geoid’s role in monitoring sea level changes becomes even more critical. It aids in assessing the impact of climate change on coastlines and vulnerable regions.
Conclusion
The geoid, a concept often overlooked by the casual observer, holds the key to unlocking profound insights into the Earth’s shape and gravitational dynamics. It serves as a bridge between theory and practical applications, impacting fields ranging from navigation to climate science. As we delve deeper into the geoid’s complexities, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of our planet’s intricacies.
FAQs
The geoid provides a reference for monitoring sea level changes by accounting for gravitational anomalies and helping scientists assess rising sea levels.
Absolutely, the geoid’s insights into gravitational anomalies can aid in identifying subsurface geological structures, minerals, and resources.
No, the geoid’s shape varies due to factors like Earth’s rotation, density variations, and tides, making it a dynamic reference surface.
Satellites orbit around the Earth’s center of mass, which is closely related to the geoid’s shape. Deviations from a simple ellipsoid influence satellite trajectories.
Yes, by studying the geoid and its variations, scientists can gain insights into the Earth’s geological history and the processes that shaped its surface.
